In modern manufacturing and quality control, precision measurement is crucial. Accurate measurement ensures that parts meet strict specifications, fit into larger components, and function properly. When it comes to measuring the physical dimensions of objects, two types of machines stand out: Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) and Vision Measuring Machines (VMMs). Though their names sound similar, these machines use different technologies and have distinct advantages depending on the application. In this article, we’ll compare the two, highlighting their unique capabilities, applications, and when to use each.

What is a CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine)?
A Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) is a precision tool used to measure the physical geometrical characteristics of an object. It uses a probe to touch the surface of a part and records its coordinates in 3D space (X, Y, and Z axes). These measurements are then processed to create detailed reports and models.
How CMM Works:
CMMs are equipped with various types of probes, such as mechanical touch probes, optical probes, and laser sensors. The probe moves along the axes and collects dimensional data, which is then converted into a 3D model or data report.
Applications of CMMs:
CMMs are widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and machining for tasks such as:
- Automotive: Checking the alignment and dimensions of engine parts.
- Aerospace: Measuring turbine blades and other complex components.
- Machining: Verifying the accuracy of fabricated parts.
Advantages of CMMs:
- High Accuracy: CMMs are known for their micrometer-level accuracy.
- Versatility: They can measure multiple dimensions, including size, shape, and position.
- Advanced Capabilities: Modern CMMs can be automated, improving consistency and efficiency.
What is a VMM (Vision Measuring Machine)?
On the other hand, a Vision Measuring Machine (VMM) is a tool that uses optical sensors and cameras to measure parts. Unlike CMMs, VMMs employ non-contact measurement methods, which are useful for delicate or soft materials that could be damaged by direct physical contact.
How VMM Works:
VMMs shine light onto a part’s surface and capture the reflected image with high-resolution cameras. The captured images are then processed by software to calculate dimensions and other features.
Applications of VMMs:
VMMs are ideal for measuring small, lightweight, or delicate parts. They are commonly used in industries like:
- Electronics: Measuring tiny components such as circuit boards.
- Medical Devices: Ensuring the precision of intricate medical instruments.
- Plastic Parts: Inspecting injection-molded components.
Advantages?of VMMs:
- Non-Contact Measurement: Ideal for fragile or soft materials.
- Speed: VMMs can perform fast measurements, making them suitable for high-volume production.
- Detailed Imaging: Capable of capturing complex shapes and small parts.

Key Differences Between CMM and VMM
Now that we’ve discussed both machines, let’s dive into their key differences. These differences are important when deciding which machine to use for your specific needs.
Measurement Method:
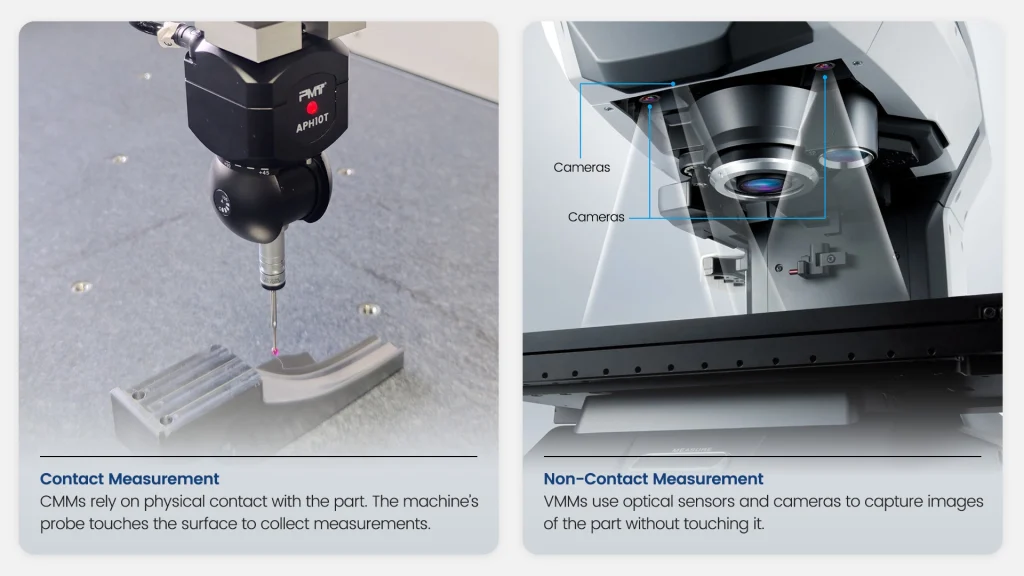
CMM: CMMs rely on physical contact?with the part. The machine’s probe touches the surface to collect measurements.
VMM: VMMs use optical sensors?and cameras?to capture images of the part without touching it.
Parts Suitability:
CMM: Best for rigid parts that can withstand physical contact. CMMs are not suitable for delicate or soft materials.
VMM: Ideal for delicate, deformable, or soft parts that could be damaged by contact-based measurements.
Accuracy:
CMM: Known for high accuracy—ideal for parts requiring micron-level precision, including 3D features and GD&T measurements.
VMM: While VMMs offer good accuracy, they are generally better suited for smaller or simpler parts and are less accurate for large, complex geometries.
Speed:
CMM: CMMs are typically slower because they measure one part at a time and are best suited for complex or large parts.
VMM: VMMs are faster, capable of measuring multiple parts simultaneously, making them perfect for high-volume production.
Workpiece Weight:
CMM: Can handle larger, heavier parts, with the capacity to measure components weighing up to 500kg.
VMM: Generally limited to lighter parts, typically under 20kg.
Cost:
CMM: CMMs tend to have a higher initial cost and maintenance requirements due to their mechanical complexity.
VMM: VMMs are typically more affordable and have lower maintenance costs.
Operator Skills:
CMM: Operating a CMM requires a skilled operator who understands how to set up and use the machine properly, especially for complex measurements.
VMM: VMMs are easier to operate, and less specialized training is needed.
When to Use CMM vs VMM
Choosing between a CMM and a VMM depends on several factors. Here’s when you should use each machine:
Use CMM When:
- Precise, 3D measurements are required for complex or large parts.
- You need to measure parts with specific GD&T features (e.g., flatness, parallelism, angularity).
- The parts are rigid and can withstand the probe’s contact.
Use VMM When:
- Measuring small, delicate, or soft parts that require non-contact measurement.
- Speed is a priority, and you need to measure multiple parts quickly in high-volume production.
- The parts are lightweight and do not require complex 3D measurements.
Conclusion
Both CMMs and VMMs are critical tools in ensuring product quality and precision in manufacturing. Each machine has unique capabilities that make it better suited for different tasks. CMMs offer high precision and versatility, making them ideal for complex or heavy parts, while VMMs provide fast, non-contact measurements, perfect for small, delicate, and high-volume parts.
Choosing the right measurement tool depends on the specific needs of your production process. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both machines, manufacturers can make more informed decisions and achieve better results in their quality control processes.
If you’re looking for a precise and efficient solution for your measurement needs, contact PMT?for expert advice on selecting the right CMM or VMM for your business. We provide comprehensive measurement systems, calibration services, and technical support to help you maintain the highest standards in manufacturing. Reach out today for a consultation!
